Splunk general
What is Splunk?
– Translate machine data into human readable
– Splunk Free license allows only 500MB per day
Deployment Models:

How Splunk Stores Data:
- – Splunk processes raw data then store that in the indexer. Indexer is pretty much a repository for Splunk data.
- – Splunk transforms incoming data into events, and store it in indexes.
- – An event is a single row of data
- > Data is specified by fields (key=value pairs)
- > Splunk adds defaults values to all events. Default values include: timestamp, host, source and sorucetype
- – Splunk stores index data in buckets

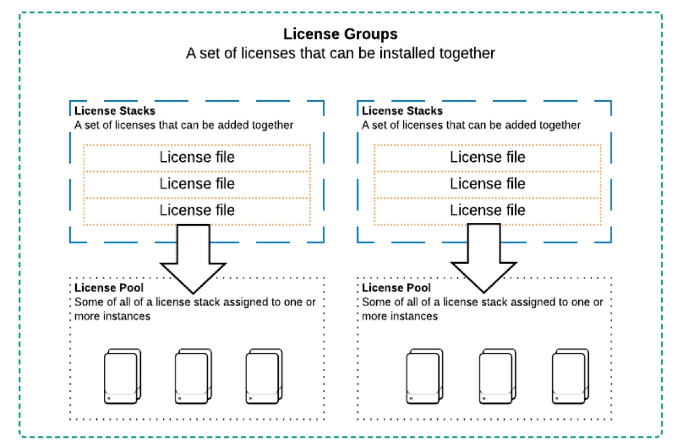
Splunk Licensing:
- – License data is ingested per day, not data stored
- – Daily indexing volume is measured from midnight to midnight by the clock on the license master
- – License pools are created from license stacks
- – Pools are sized for specific purposes
- – Managed by the license master
- – Indexers and other Splunk Enterprise instances are assigned to a pool
- – Recommended not assigning Forwarder to the license pool because it has unique license type
Splunk Apps:
- – Review “apps.pdf”
- – An app is a collection of splunk configuration files
- – An add-on is a subset of an app
- – Apps are downloaded from Splunkbase.com or splunkbase.splunk.com
Installing Splunk:
- – Download the package from Splunk website or with wget command (e.g. Splunk 8.0.5):
- # wget -O splunk-8.0.5-a1a6394cc5ae-linux-2.6-x86_64.rpm ‘https://www.splunk.com/bin/splunk/DownloadActivityServlet?architecture=x86_64&platform=linux&version=8.0.5&product=splunk&filename=splunk-8.0.5-a1a6394cc5ae-linux-2.6-x86_64.rpm&wget=true’
- – To start Splunk
- # /opt/splunk/bin/splunk start –accept-license
Getting Data In: How Splunk Consumes Data:
- Review “getdatain.pdf”.
- HTTP Event collector (HEC)
- Send data and application logs to Splunk over HTTP(s)
- Token based authentication
- No forwarder needed
Forwarders: Forwarding & Receiving:
- Review “universalforwarders.pdf”.
- Simple Forwarding and Receiving setup
- Login to Search Head’s web GUI
- Select “Setting” -> “Data” -> “Forwarding and Receiving” -> “Receive Data” -> “Configure Receiving”
- Click “New Receiving Port”
- Enter default port “9997” then save
- Login to Heavy Forwarder’s Web GUI
- Select “Setting” -> “Data” -> “Forwarding and Receiving” -> “Forward Data” -> “Configure forwarding”
- Click “New Forwarding Host”
- Enter <Indexer’s IP or hostname>:<9997>
- Apply forwarding license by select “Settings” -> “System” -> “Licensing”
- Select “Change license group”
- Select “Forwarder license”
- Save then restart
- Monitor data configurations
- Select “Settings” -> “Add data”
- Select “Monitor” -> “File and Directory”
- Following thru the wizard
- Verify logs in Search Head
- Download and install Splunk Universal Forwarder:
- For Linux:
- Un-tar the Splunk Universal Forwarder tar ball file (e.g. splunkforwarder-8.2.2-87344edfcdb4-Linux-x86_64.tgz) to /opt directory.
- Start Splunk daemon at system boot:
- # {splunk_home}/bin/splunk enable boot-start
- Start the Splunk daemon same way as full Splunk install.
- # {splunk_home}/bin/splunk start –accept-license
- Review current forward server:
- # {splunk_home}/bin/splunk list forward-server
- Add Splunk forwarder server:
- # {splunk_home}/bin/splunk add forward-server <10.0.01:9997>
- Review current monitor directories:
- # {splunk_home}/bin/splunk list monitor
- Add monitor target:
- # {splunk_home}/bin/splunk add monitor </var>
- Restart splunkd
- For Windows: Follow the wizard prompts.